Have you ever wondered what exactly makes up your DNA? or how energy is transferred and stored in your cells? A class of small but potent chemicals known as nucleotides holds the key to the solution. For life as we know it, these molecular building components are essential.
Let us examine nucleotides in detail, including their definition, mechanism of action, and significance.
Describe nucleotides.
Fundamental Definition
Small chemical molecules called nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA. In a genomic tower, each nucleotide is comparable to a Lego block.
Function in Biology
They are essential for energy transmission, cell signaling, and enzyme function in addition to being structural components of DNA and RNA.
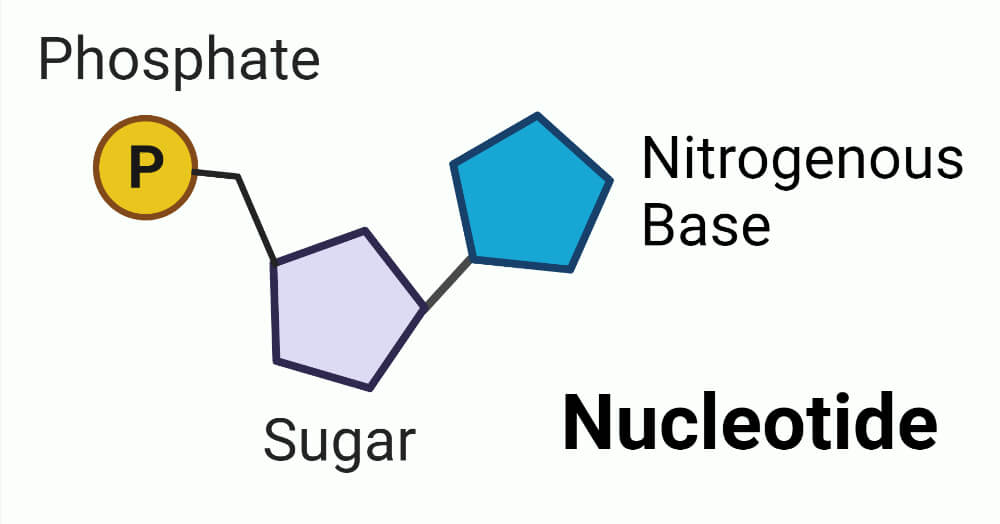
Nucleotide Chemical Structure
There are three components to each nucleotide:
Base of Nitrogen
This is where the information is carried. Purines and pyrimidines are its two tastes.
Sugar Pentose
In RNA, the sugar is ribose; in DNA, it is deoxyribose. It keeps everything in place.
Group Phosphate
One to three phosphate groups are often joined. They are in charge of transferring energy; consider ATP.
Types of Nitrogenous Bases
Purines
These are larger double-ring structures. The purines are:
-
Adenine (A)
-
Guanine (G)
Pyrimidines
These are single-ring structures:
-
Cytosine (C)
-
Thymine (T) – Found only in DNA
-
Uracil (U) – Found only in RNA
Nucleotides vs Nucleosides
Confused between the two? You’re not alone.
-
A nucleoside = nitrogenous base + sugar
-
A nucleotide = nucleoside + phosphate
Think of a nucleotide as a nucleoside with a power boost.
Functions of Nucleotides
DNA and RNA Building Blocks
Nucleotides are strung together to form long chains of DNA and RNA, which store genetic information.
Energy Transfer (ATP, GTP)
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) is the cell’s energy currency. When a phosphate bond breaks, energy is released.
Signaling Molecules (cAMP, cGMP)
Nucleotides also act as messengers in your body. cAMP helps regulate heart rate, memory, and more.
Coenzymes (NAD+, FAD)
These modified nucleotides assist enzymes in metabolism, especially in producing energy from food.
Nucleotide Metabolism
Your body is constantly making and breaking down nucleotides.
Synthesis (De Novo and Salvage Pathways)
-
De novo synthesis builds nucleotides from scratch.
-
Salvage pathways recycle components from broken-down nucleotides.
Degradation
Excess nucleotides are broken down, and waste products like uric acid are excreted.
DNA and RNA: Made of Nucleotides
DNA Nucleotides
These include adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. They’re linked in a double helix that stores all your genetic code.
RNA Nucleotides
Here, uracil replaces thymine. RNA plays several roles, including carrying genetic instructions and helping make proteins.
Importance of Nucleotides in Genetics
Mutations in nucleotide sequences can lead to genetic disorders or beneficial traits. They’re the “letters” in your genetic alphabet.
Synthetic and Modified Nucleotides
In Research and Medicine
Scientists use synthetic nucleotides in PCR, gene editing, and developing mRNA vaccines (like for COVID-19). Modified nucleotides can enhance stability and function in biotech and medicine.
Dietary Sources of Nucleotides
While your body makes its own, nucleotides are also found in:
-
Organ meats
-
Fish
-
Mushrooms
-
Legumes
These foods may support immune and gut health, especially in infants and during recovery.
Disorders Related to Nucleotide Metabolism
Gout
Excess breakdown of purines increases uric acid, which can crystallize in joints—causing painful gout.
SCID (Severe Combined Immunodeficiency)
Caused by faulty nucleotide metabolism, this disorder leaves the immune system severely compromised.
Role in Evolution and Life’s Origin
Nucleotides may have formed spontaneously on early Earth, forming the basis of RNA World Hypothesis—a theory that life began with self-replicating RNA molecules.
Nucleotides in Modern Medicine
-
Used in gene therapy
-
Basis for mRNA vaccines
-
Targeted in anticancer drugs and antivirals
They’re a hot topic in both biotechnology and pharmacology.
Nucleotides are the unsung heroes of biology. From powering your cells to storing your genetic blueprint, they play countless roles that keep life ticking. Whether you’re looking to understand health, genetics, or molecular biology, knowing about nucleotides gives you a solid foundation.




